MCE’s Energy 101 Series focuses on the why and how of renewable energy so that you can learn more about concepts like the benefits of biomass and the science behind solar. Looking for more? Check out the links in this blog to read more about Energy 101 or to dive deeper into our Energy Expert series.
Ever wonder how the energy that powers our daily lives gets to you? A lot goes on behind the scenes to make sure that electricity is readily available to meet your needs. Your first step is learning about how power is generated, distributed to homes, and used by customers like you.
The Electric Grid
The ability to flip a switch and have power in your home is relatively new. Early days of electricity generation required power sources to be directly next to the devices they powered and were often run on coal. It wasn’t until the 1920s that the United States had an electrical grid similar to the one we have today.
The transition to a centralized electricity generation grid allowed power to be created on a much larger scale, with electricity from larger power plants traveling miles to reach customers in their homes and throughout our infrastructure. Today we use electricity in almost every aspect of our lives, but we may never consider how that power gets to us.
Generation
Electricity is generated by harnessing the energy from natural resources, such as renewable fuels (solar, wind, and biomass) or nonrenewable fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas). The most important point about electric generation is that, no matter where or how your power is being produced, it all runs into the same electrical grid.
Transmission and Distribution
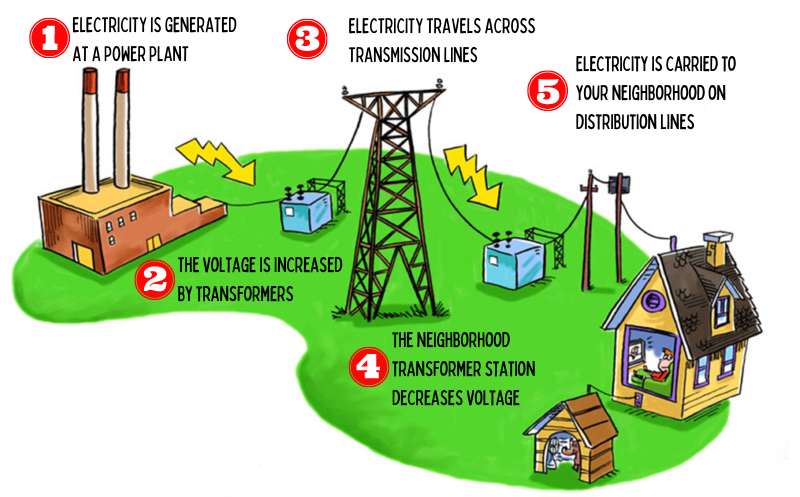
The first step for energy on the electric grid is transmission. Transmission carries energy across long distances in high-voltage power lines.
Distribution occurs when you pull energy into buildings or vehicles. When you turn on electric devices in your home, power moves from those high-voltage lines through a local substation. At the substation, the voltage is lowered by transformers, making it possible for the energy to be safely used by a home, business, or electric vehicle. This low-voltage energy is then distributed through smaller lines in your local neighborhood.
Energy Billing and Metering
When the energy reaches your home or business, it flows through a meter that keeps track of how much electricity is being used at your property. The meter not only helps your power provider keep track of how much to charge you, but it also helps them generate the right amount of energy to meet your needs.
How Do I Know Where My Power Comes From?
In order to receive electricity in your home or business, an energy service provider like MCE buys energy from large generation facilities on your behalf. This power can be from any type of generation resource. Generation will be covered in greater detail in upcoming Energy 101 posts.
Think of the electric grid like a bathtub and electricity generation like adding water. As you add water (power) to the bathtub, you can’t tell one water molecule (electron) from another. However, you can tell how clean the water in the bathtub is. The same principle applies to the electric grid. While you can’t definitively say which energy resource generated the electrons that are powering your fridge, you can say that you’re making the electric grid cleaner by choosing a more renewable energy service option instead of an option that puts more polluting sources of energy onto the grid.
Check out MCE’s power content label to see where the energy you use comes from.
If I Have Solar, Do I Still Use the Grid?
If you’re a residential or business customer and generate your own solar electricity, that’s great! Small-scale solar generation is becoming more common across the United States, and in 2020 the State of California required all new-construction, single-family homes and multifamily homes under four stories to include solar. This requirement helps reduce energy costs for property owners and renters and adds clean energy to the power grid during the day. Since solar panels produce electricity when the sun is shining, alternate sources of energy are needed when the sun goes down.
When the sun sets, homes with solar pull electricity from the grid. Electricity coming into your home is generated from the nearest power source, such as wind, biomass, hydroelectric, or natural gas. One hundred percent renewable service options, like MCE Deep Green, ensure that all of your household or business electricity needs for the year are matched with renewable energy generated in California.






