Photo: Damian and family, Novato residents and MCE rebate recipients.
Benefits of Driving an EV
EV Models & Types
There are three main types of EVs:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs, commonly known as EVs) – powered solely by electricity
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) – can run on either electricity or gasoline
- Hydrogen Fuel-Cell Vehicles (FCVs) – use hydrogen gas to generate electricity that powers an electric motor
TIP: Compare the range of EV models with your daily commute or your typical trip distance. Get other resources and helpful information for Buying and Driving an EV (pdf).
Rebates & Incentives
EV Charging
Charging at Home
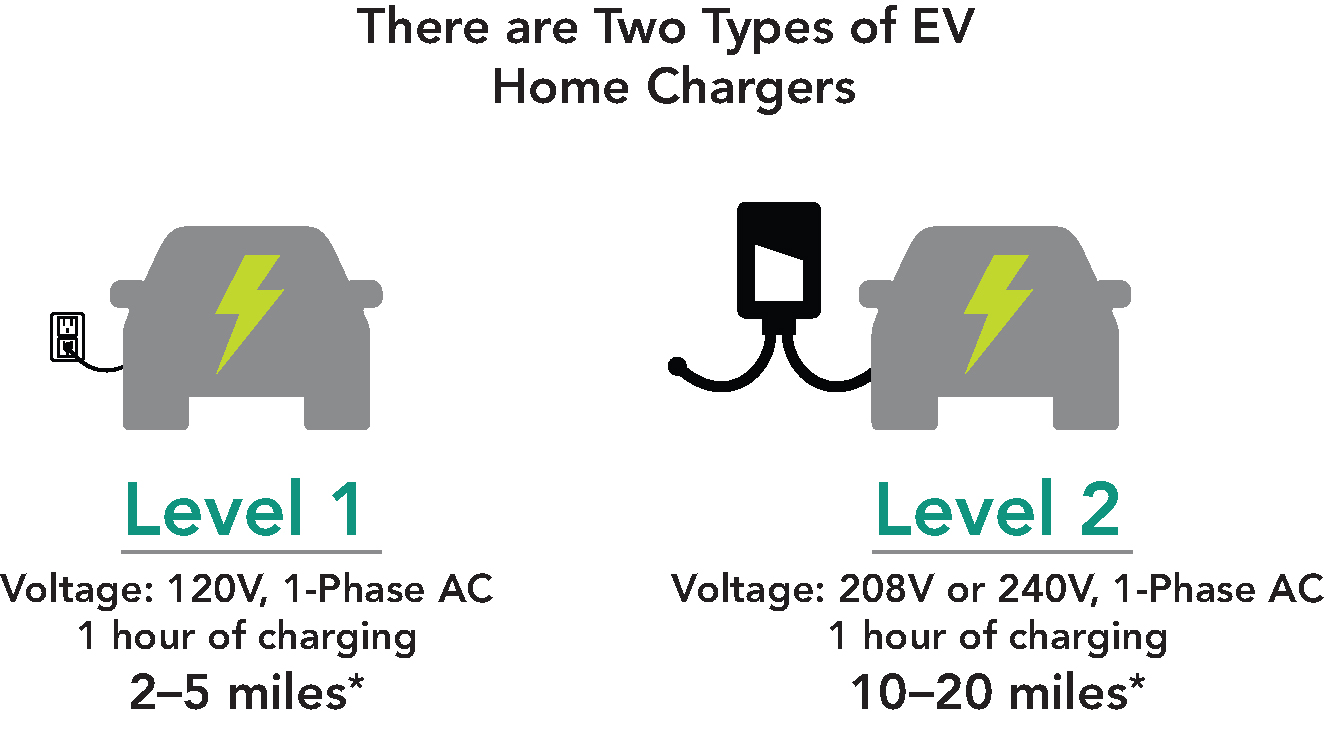
EVs come with a Level 1 charger that can simply be plugged into a regular home outlet. You can also upgrade to a Level 2 charger for a faster charge. A Level 2 charger requires the same type of outlet used for washing machines and ovens and can be easily installed by an electrician.
Electricity Rates
If you plan to charge at home often, we recommend that you compare your current electricity rate to other options and choose the one that’s best for you. Rates apply to your household’s entire electricity usage, not only your EV charging. Compare your options by logging into your PG&E online account or calling PG&E at 1 (866) 743-0335.
TIP: Save money on EV charging by powering up outside of 4–9 pm when rates are highest. Sustainability fans, charge from 12–4 pm to soak up daytime solar and take advantage of the increased renewable energy on the grid.
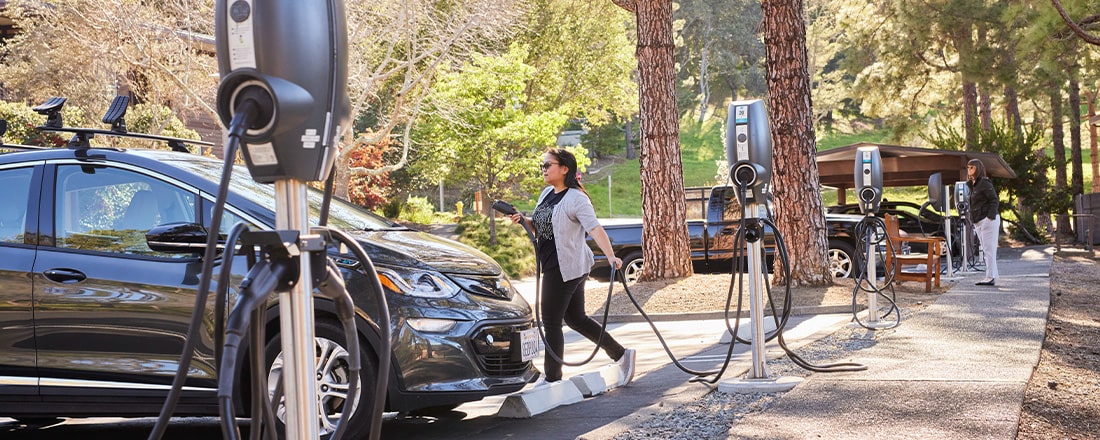
Charging on the Road
There are a lot of public charging options with more opening every week. Use the Plugshare map to locate an EV charging station near you or along your route.
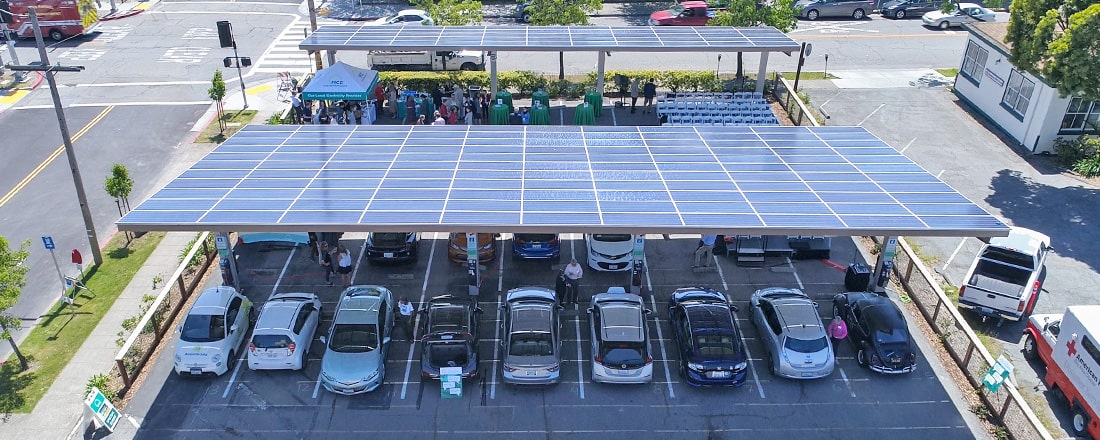
If you manage a workplace or multifamily property, see if your site qualifies for MCE’s EV charging rebate.
FAQ
When combined with rebates and incentives as well as the cost of fuel and maintenance, owning an EV is often less expensive to operate than a gas-fueled car. Depending on your eligibility, you could receive thousands of dollars13,750 in rebates for an EV – even more if you trade in an older vehicle – and up to $2,000 in rebates for EV charging.
In terms of the cost of fuel and maintenance, gas car drivers pay twice as much for fuel. Driving an EV can save you over $650 each year. Plus EVs don’t require the kind of regular maintenance that gas cars do. The only regular maintenance EVs need is adjusting tire pressure and rotating the tires, saving EV drivers a lot more money.
Used EVs can even be as low as $2,000 if you qualify for income-based incentives.
Every EV comes with a Level 1 charger that can be plugged into the same 120V outlet that you charge your everyday devices. For the average Bay Area commuter, you can plug in your EV overnight (midnight – 8 AM) and charge up what you used the day before. Learn more about charging an EV at home.
Yes, EVs undergo the same rigorous safety tests as traditional gas-fueled cars with additional standards for battery safety.
Yes, replacing a gas-fueled car with an EV and charging up with MCE’s Deep Green 100% renewable electricity is an 82% reduction in emissions! That comparison includes vehicle manufacturing, battery manufacturing, gas/electricity production and consumption, and maintenance.






