One of the most underrated benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) is being able to permanently remove “go to the gas station” from your Errands To Do List. With an EV, you can “refuel” at the most convenient place: your home. Home EV charging is easy to set up, but can be new territory for some EV drivers.
Here we’ll answer the most commonly asked questions about EV charging at home.
1. What types of home chargers are there?
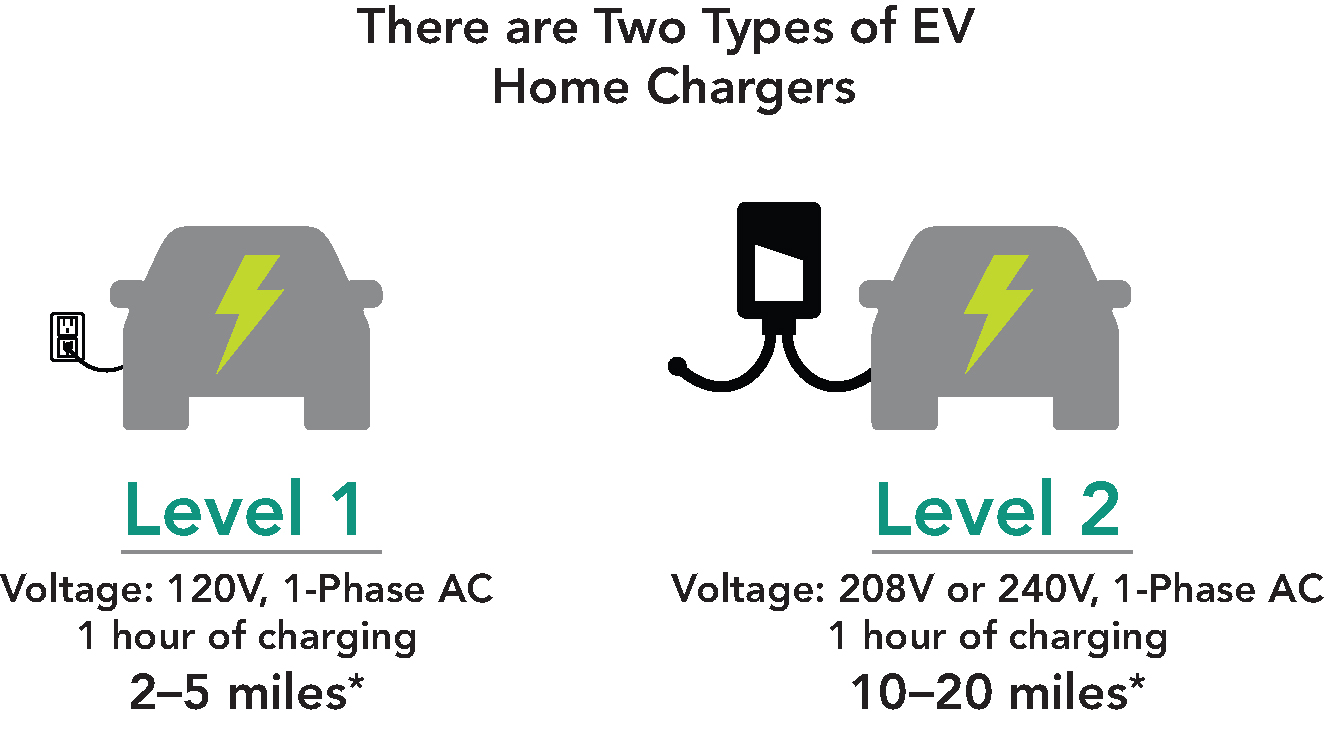
Level 1 chargers use 120-volt (120V) outlets, which are the standard socket types we use to plug-in lamps, toasters, and other small appliances. That’s right, your wall sockets can charge an EV!
Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, require a 240-volt (240V) outlet, which is the type used for larger appliances like ovens and clothes dryers.
2. How much time does it take to fully charge an EV battery?
Level 1 chargers, aka standard home outlet compatible chargers, will typically charge an EV overnight for the average Bay Area commute. While sleep recharges and refreshes you, electricity is recharging your EV battery!
Level 2 chargers take less time to charge an EV – about half the time of a Level 1 charger, on average.
3. Which type of charger is better?
This depends on your needs, your budget, and your home’s electrical panel.
Level 1: A standard 120V home outlet will charge the average Bay Area commuter’s EV and doesn’t require any electrical improvements.
Level 2: A Level 2 charger allows for faster EV charging at home, but requires a 240V outlet where you park your car. Not all homes have this type of outlet in a spot accessible to your car, so you’ll need to contact an electrician to determine whether your electrical panel has the capacity to add this type of outlet, or if you’ll need a panel upgrade.
4. How much does EV charging cost compared to gas?
Gas is 200% more expensive than charging your EV at home with MCE’s Deep Green 100% renewable service option, as discussed in our recent blog post, Top 3 Ways EVs Save You Money.
Why? Not only does renewable electricity for an EV cost less annually than the gas for your car, MCE’s EV rate (called “EV2”) helps make charging more affordable. You can plug in an EV and schedule it to charge during “off-peak” hours, from Midnight to 3pm, when electricity is less expensive. Bonus: your EV battery will be charged when you wake up the next morning!
5. What if I rent, or charging at home just isn’t an option?
Nearly half of us rent in the Bay Area** and we might not be the decision-maker about building improvements like adding an outlet or, better yet, EV charger at parking spaces. Renting doesn’t have to be a barrier to getting an EV though. MCE offers a rebate for adding charging stations to apartment buildings (aka multifamily properties) and workplaces (like office buildings and schools) to help save significantly on hardware and installation costs.
Additionally, there are over 400 public EV charging stations across MCE’s service area.
6. When is the best time to charge?
The best time to charge at home for saving money and maximizing clean energy use is between midnight and 3pm. Even better, you can set a charging timer so when you plug in at home your car will charge after midnight and still leave you with more than enough range for your commute the next day. Check your car’s user manual, or you can do an online search, like “(EV brand name), set your charging schedule.”
While MCE offers standard Light Green 60% renewable or Deep Green 100% renewable electricity options, overall the California grid has the “dirtiest” power between 4pm-9pm,*** so you’ll want to avoid charging during these peak demand times.
As the sun starts setting, the natural gas plants are turning on. You can help reduce California’s natural gas use by charging when the sun is shining because there’s plenty of solar energy on the grid, plus you’ll get the benefit of lower electricity rates between midnight and 3pm. You can also save money on your electricity during that period of time by switching to MCE’s EV2 rate.
7. What if I lose power, or my power is shut off?
Gas cars face the same challenges as EVs during power outages. No one can fill up with gas when the power goes out because gas pumps are powered by electricity too.
PG&E usually gives customers 24-48 hours advance notice of a Public Safety Power Shutoff event. Plugging a Level 1 charger into a 120V outlet (aka standard wall socket) for 24 hours will provide over 72 miles of range on average. If you have a Level 2 charger at home, your car will typically be fully charged within 24 hours. When the power goes out and gas car drivers are lining up at the pump, you’ll already be ready to go.
8. How do I install a Level 2 charger and are there any incentives?
PG&E’s Home Charger Resource Project can help you identify what charger level is best for you and offers resources, including an installation checklist and a list of qualified installers in your area. Want to upgrade to a Level 2 home charger? Check out the models and incentives through Electric For All, a California non-profit initiative.
We hope this answers your questions about how EV charging actually works! If you have any other questions, please reach out to info@mceCleanEnergy.org.






