MCE’s Energy 101 Series focuses on the why and how of renewable energy so that you can learn more about concepts like the benefits of biomass and the science behind solar. Looking for more? Check out the links in this blog to read more about Energy 101 or to dive deeper into our Energy Expert series.
An electric vehicle (EV) is any vehicle that can be plugged in and be fully or partly powered by electricity. EVs have a lower impact on the environment than gas-powered vehicles and help drivers save money on gas and vehicle maintenance.
What are the types of EVs?
There are three main types of EVs: battery electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, and gas hybrid vehicles. EV most commonly refers to the first type (battery EVs).
Battery Electric Vehicles
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) run solely on a battery charge and produce no tailpipe emissions. The BEV charging port looks like the port on traditional gas vehicles. However, the car is connected to a power supply and charged with electricity from the grid.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) run on electricity and use gas as backup. These vehicles can be charged at a normal EV charging station and can also be filled with gasoline. When the battery is depleted, plug-in hybrids automatically switch to the gas combustion engine and produce tailpipe emissions.
Gas Hybrid Vehicles
Gas hybrid vehicles (hybrids) have electric components to reduce gas consumption, but run solely on gas. Hybrid cars have an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. The electric motor runs on batteries that are charged through the engine and regenerative braking. Support from the electric motor offers the same vehicle performance while using less fuel.
How do you charge EVs?
Unlike gas-powered vehicles that require a visit to the gas station, you can refuel EVs anywhere there is electricity.
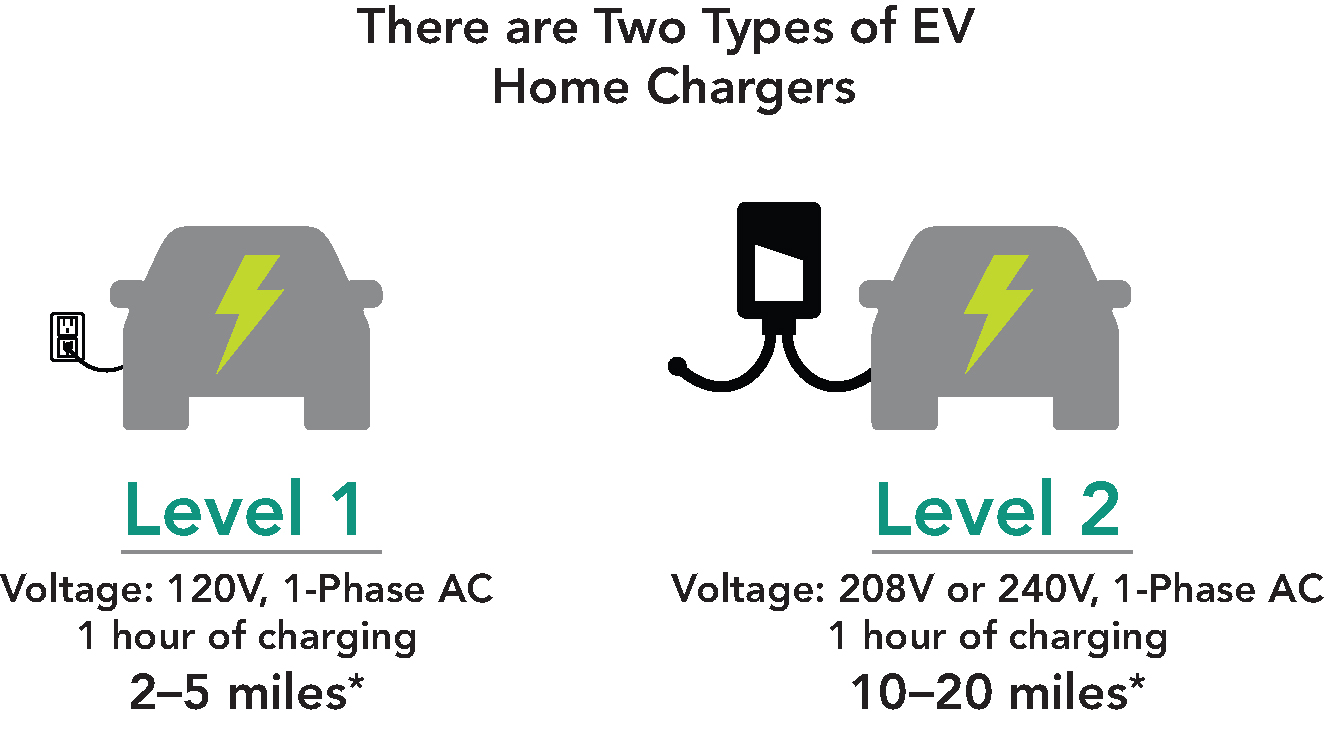
Charging at Home
You can charge EVs at home with a regular 120-volt outlet. This Level 1 charging can typically charge your EV overnight for the average Bay Area commute. You can also upgrade to a 240-volt outlet for Level 2 charging, which takes around half the time of Level 1 charging.
Charging Away from Home
EV charging stations are in grocery store or shopping center parking lots, parking garages, workplaces, highway rest stops, public parks, and more. Some locations even have fast chargers to power your car in as little as 30 minutes. MCE is currently offering free EV charging at our San Rafael office. Download the Greenlots app and make an account to charge at MCE. To find an EV charging station near you, visit the PlugShare map on MCE’s website or use your preferred EV charging station locator app or map.
Are EVs cleaner than gas-powered vehicles?
EVs run on electricity instead of diesel or gas and produce less emissions than a gas-powered car, or no tailpipe emissions at all. The total emissions from driving EVs depend on the local electricity supply. However, EVs are a cleaner option than gas-powered vehicles in every region of the United States, regardless of power breakdown, because they’re extremely fuel efficient. While gas-powered vehicles use only 14-26% of the energy from gasoline, EVs can utilize up to 80% of the energy in its battery. EVs will become cleaner each year as the United States puts more renewable energy on the grid. Residents in MCE’s service area can power their EVs with 100% renewable energy when they opt up to MCE’s Deep Green energy service.
Can we electrify other vehicles?
Medium- and heavy-duty vehicles such as buses, trucks, vans, and tractors are responsible for around 24% of transportation emissions in the United States. Electrifying these commercial vehicles is a critical step in reaching zero-emission goals. In addition to reducing emissions, electric commercial vehicles require less servicing and are quieter than conventional commercial vehicles. Increased incentives, advancements in battery technology, and more developed charging infrastructure will accelerate the electrification of medium- and heavy-duty vehicles.
How does MCE support electric vehicle adoption?
MCE is working to increase the adoption of electric vehicles through EV and EV charging incentives. MCE offers a $3,500 rebate for qualifying customers to purchase or lease new EVs. MCE can also help qualifying customers combine the rebate with federal, state, and local incentives. MCE’s EV charging rebate program covers both large and small charging projects (2−20+ ports). The program allows market rate and affordable multifamily properties and workplaces to save up to $3,000 per port. If the properties opt up to Deep Green 100% renewable energy, they can get an additional $500 per charging port. MCE also provides technical assistance during the application and installation processes.






