MCE’s Energy 101 series focuses on the why and how of renewable energy so that you can learn more about concepts like the benefits of biomass and the science behind solar. Looking for more? Check out the links in this blog to read more about Energy 101 or to dive deeper into our Energy Expert series.
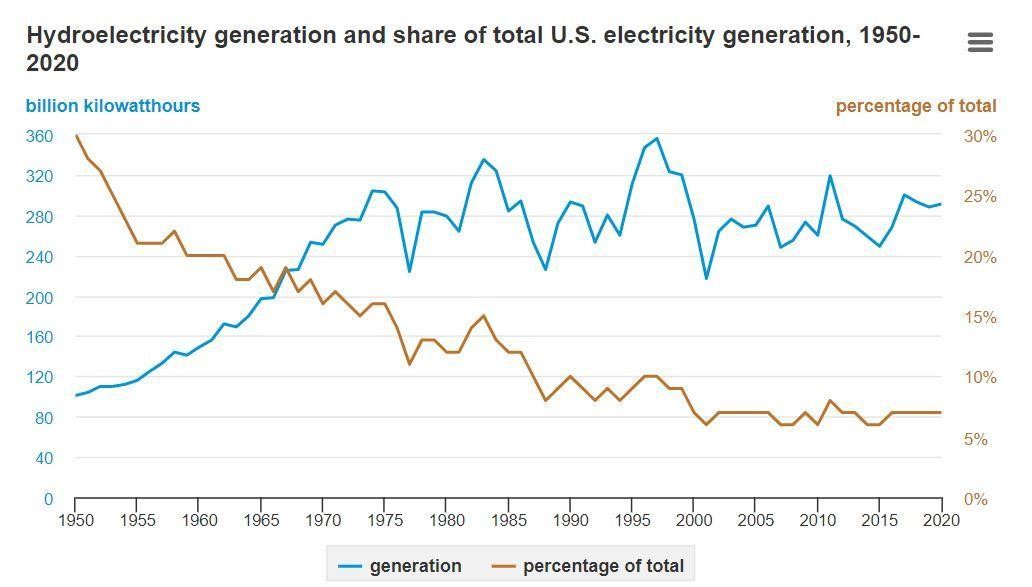
The power of moving water has been used as an energy source for over two millennia. The hydropower plants that we use today harness kinetic energy from moving water and transform it into electricity. As of 2019, up to 35.4% of MCE’s Light Green energy service came from hydroelectric energy sources
What are the advantages of hydroelectric?
- It’s one of the least expensive power sources.
- It’s reliable and can produce energy around the clock.
- Hydroelectric plants are extremely efficient and can convert up to 90% of energy into electricity.
- Hydropower doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or waste.
What are the disadvantages of hydroelectric?
- Hydroelectric power is dependent on water level and fluctuates based on precipitation levels.
- It disturbs natural habitats, can disturb the migration of fish, and can harm native plants and animals.
- Reservoir and dam construction can displace communities and increase the risk of flooding.
How is hydropower converted into electricity?
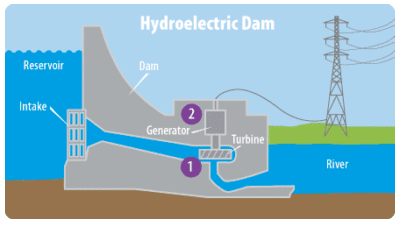
Hydroelectric dam
Hydroelectric dams fill a reservoir by restricting the downstream flow of water. Water flows downhill through a small opening in the dam, where it spins turbines and generates mechanical energy. A generator then converts the mechanical energy into electricity.
Pumped storage
Pumped storage is a type of hydropower plant that allows energy generated by wind and solar resources to be stored during times of low demand until it’s needed. Wind or solar energy are used to pump water uphill to a reservoir when demand for electricity is low and generating power is high. The water is released and spins turbines as it runs back downhill to generate electricity during times of high demand.
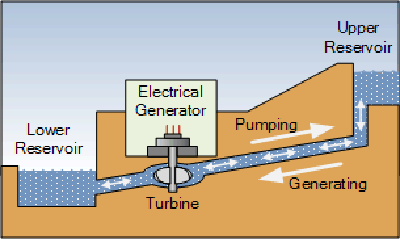
(Graphic: Alternative Energy Tutorials)
Run-of-river plants
Run-of-river hydroelectric plants utilize the natural flow of water down a river as opposed to a large reservoir. Because they lack water storage, run-of-river plants rely on seasonal water level and typically have a lower generating capacity. These plants have a smaller environmental footprint than hydroelectric dams and are less likely to cause flooding.
What is the difference between large hydro and small hydro?
Hydropower plants vary in size and generation capacity. Large hydropower plants are large-scale dams that have a capacity of over 30 megawatts, whereas small hydropower plants typically generate under 10 megawatts.
Why isn’t large hydro considered a renewable energy source?
Both small and large hydroelectric plants are considered carbon-free sources of electricity. Small hydro plants are also classified as renewable. However, large plants aren’t considered renewable in the State of California because they disrupt the surrounding environment. Carbon-free resources like small and large hydro play an important role in helping MCE and California meet our climate goals.
Looking for more Energy 101 blogs? Sign up for our monthly eNewsletter to get this content and more delivered straight to your inbox.